Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
Recent spatial transcriptomics (ST) technologies have allowed us to capture cellular heterogeneity while retaining spatial information. However, ST datasets may lose single-cell resolution, limiting the discovery of cell-type-specific spatial patterns of localization and expression.
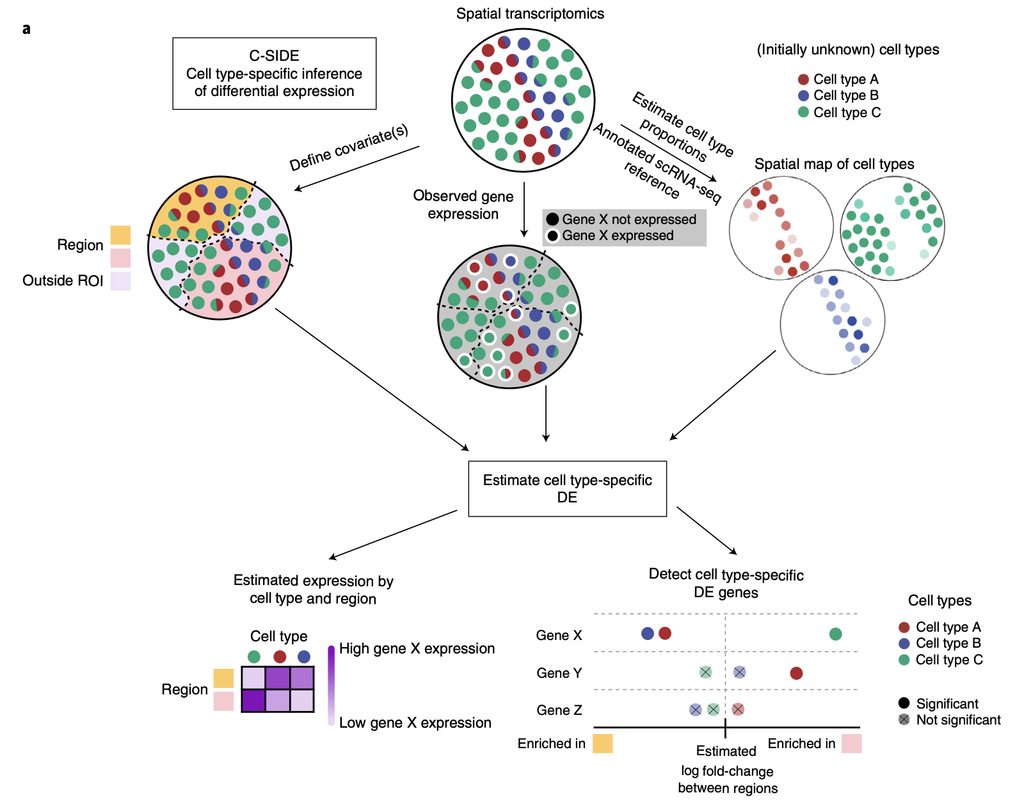
spacexr (Spatial-eXpression-R) is an R package providing two methods, i.e., Robust Cell Type Decomposition (RCTD) (Cable, Dylan M., et al., 2022) and Cell type-Specific Inference of Differential Expression (C-SIDE) (Cable, Dylan M., et al., 2022) for ST data. RCTD is proposed for cell type deconvolution, while leveraging references from another annotated single-cell RNA-seq data. C-SIDE identifies cell type-specific differential expression, accounting for localization of other cell types.
We will illustrate an example workflow in two notebooks, RCTD and C-SIDE, on a hippocampus Visium dataset provided by the authors. The notebooks are inspired from spacexr's vignettes and modified to demonstrate how the tool works on BioTuring's platform.