Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
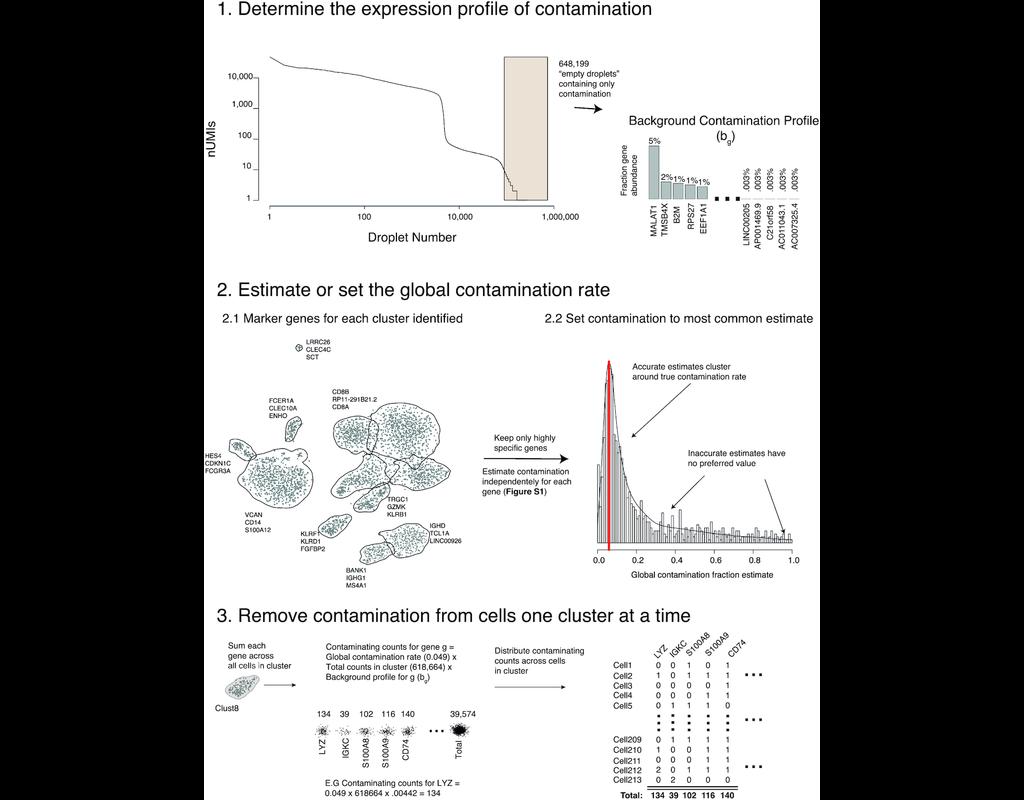
Droplet-based single-cell RNA sequence analyses assume that all acquired RNAs are endogenous to cells. However, there is a certain amount of cell-free mRNAs floating in the input solution (referred to as 'the soup'), created from cells in the input solution being lysed. These background mRNAs are then distributed into the droplets with cells and sequenced alongside them, resulting in background contamination that confounds the biological interpretation of single-cell transcriptomic data.
SoupX (Young and Behjati, 2020) is one of the methods proposed for ambient mRNA removal. In this notebook, we will illustrate a workflow example that applies SoupX to correct the ambient RNA in a dataset of 10k PBMC cells. The output of SoupX is a modified counts matrix, which can be used for any downstream analysis tool.