Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
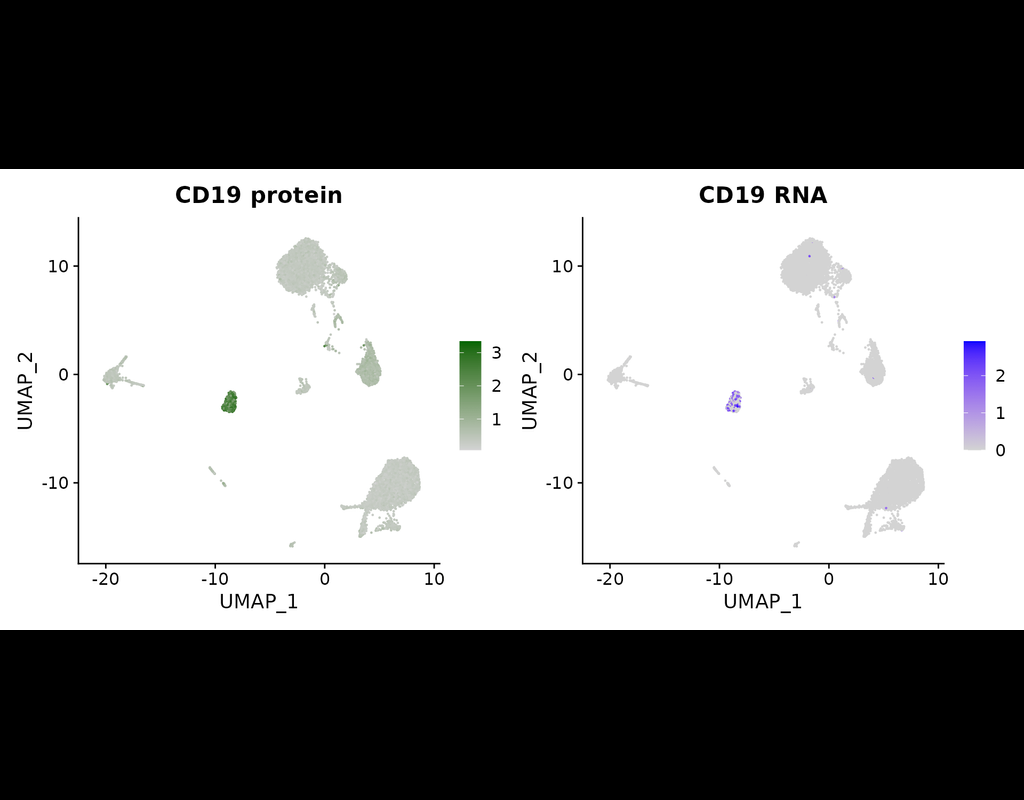
The simultaneous measurement of multiple modalities represents an exciting frontier for single-cell genomics and necessitates computational methods that can define cellular states based on multimodal data.
Here, we introduce "weighted-nearest neighbor" analysis, an unsupervised framework to learn the relative utility of each data type in each cell, enabling an integrative analysis of multiple modalities. We apply our procedure to a CITE-seq dataset of 211,000 human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with panels extending to 228 antibodies to construct a multimodal reference atlas of the circulating immune system. Multimodal analysis substantially improves our ability to resolve cell states, allowing us to identify and validate previously unreported lymphoid subpopulations.
Moreover, we demonstrate how to leverage this reference to rapidly map new datasets and to interpret immune responses to vaccination and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Our approach represents a broadly applicable strategy to analyze single-cell multimodal datasets and to look beyond the transcriptome toward a unified and multimodal definition of cellular identity.