Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
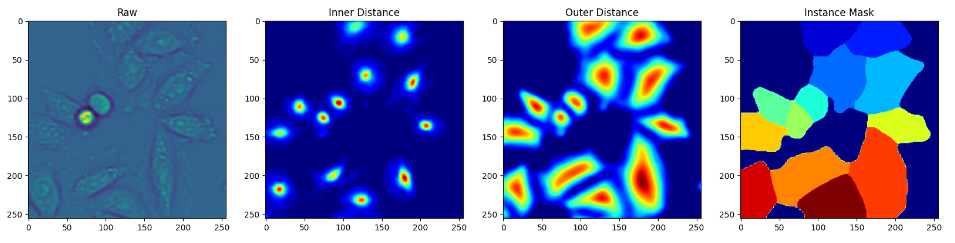
Live-cell imaging has opened an exciting window into the role cellular heterogeneity plays in dynamic, living systems. A major critical challenge for this class of experiments is the problem of image segmentation, or determining which parts of a microscope image correspond to which individual cells. Deepcell shows that deep convolutional neural networks, a supervised machine learning method, can solve this challenge for multiple cell types. The authors share their experience in designing and optimizing deep convolutional neural networks for this task and propose some design rules to achieve stable performance. The authors conclude that deep convolutional neural networks are an accurate, time-saving, applicable method for many types of cells, from bacteria to animal cells, and expand the capabilities of live-cell imaging to include multi-cell systems.
Deepcell library allows users to apply pre-existing models to imaging data as well as to develop new deep learning models for single-cell analysis. This library specializes in models for cell segmentation (whole-cell and nuclear) in 2D and 3D images as well as cell tracking in 2D time-lapse datasets. These models are applicable to data ranging from multiplexed images of tissues to dynamic live-cell imaging movies.
deepcell-tf which is written in Python using TensorFlow, is a deep learning library for single-cell analysis of biological images. It is one of several resources created by the Van Valen lab to facilitate the development and application of new deep learning methods to biology.