Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
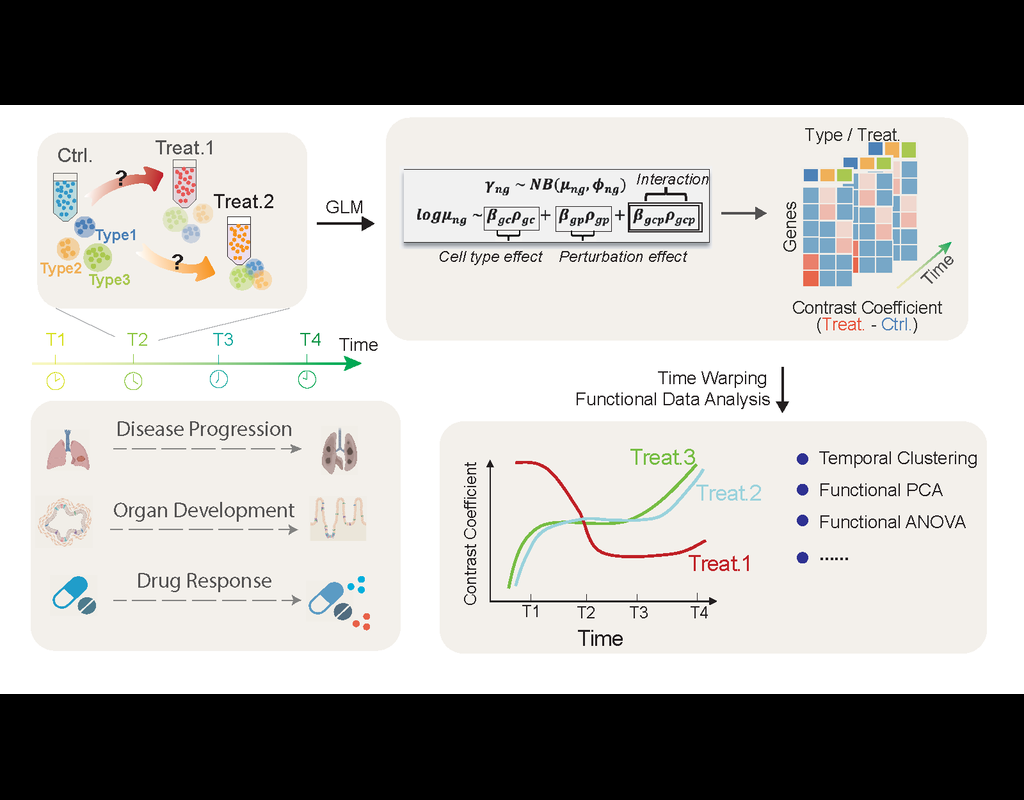
Perturbation effects on gene programs are commonly investigated in single-cell experiments. Existing models measure perturbation responses independently across time series, disregarding the temporal consistency of specific gene programs. We introduce CellDrift, a generalized linear model based functional data analysis approach to investigate temporal gene patterns in response to perturbations.
CellDrift is a python package for the evaluation of temporal perturbation effects using single-cell RNA-seq data. It includes functions below:
1. Disentangle common and cell type specific perturbation effects across time;
2. Identify patterns of genes that have similar temporal perturbation responses;
3. Prioritize genes with distinct temporal perturbation responses between perturbations or cell types;
4. Infer differential genes of perturbational states in the pseudo-time trajectories.