Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
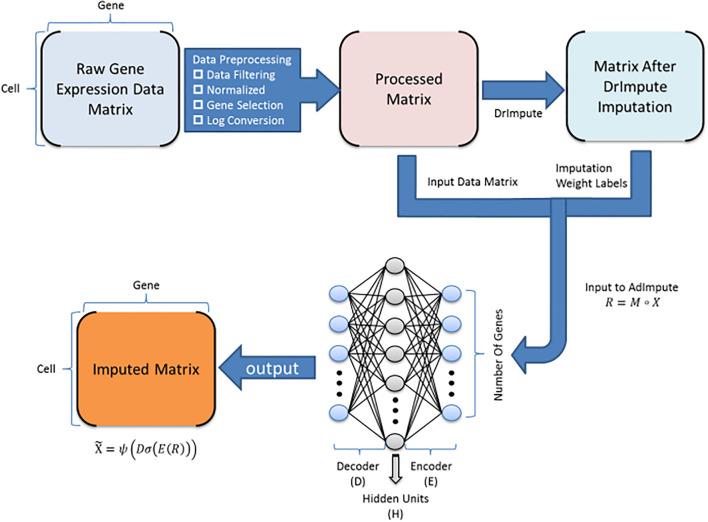
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) protocols often face challenges in measuring the expression of all genes within a cell due to various factors, such as technical noise, the sensitivity of scRNA-seq techniques, or sample quality. This limitation gives rise to a need for the prediction of unmeasured gene expression values (also known as dropout imputation) from scRNA-seq data.
ADImpute (Leote A, 2023) is an R package combining several dropout imputation methods, including two existing methods (DrImpute, SAVER), two novel implementations: Network, a gene regulatory network-based approach using gene-gene relationships learned from external data, and Baseline, a method corresponding to a sample-wide average..
This notebook is to illustrate an example workflow of ADImpute on sample datasets loaded from the package. The notebook content is inspired from ADImpute's vignette and modified to demonstrate how the tool works on BioTuring's platform.
| Notebooks |
|---|